Anti-C4d Antibody (FITC) | BI-RC4D-FITC
-
Method
For detection of cell- or solid-phase bound C4d and C4d split product by flow cytometry using FlowPRA® Class I and II screening test beads from One Lambda.
-
Sample type
Serum
-
Use
Research use only
Anti-C4d Antibody (FITC) Product Overview
The Anti-C4d FITC antibody will identify human complement split product C4d. It is suggested to be a valuable marker for humoral rejection of transplants (kidney, heart, lung). The antibody is applicable for detection of cell- or solid-phase bound C4 and C4d split product by flow cytometry using FlowPRA® Class I and II screening test beads from One Lambda, Inc.
Anti-C4d Antibody (FITC) Components
100 µl (125 tests) protein G purified polyclonal rabbit anti-human C4d antibody, FITC labeled
Storage instructions: for one month at 4°C. For prolonged period of time, aliquot and store at -20°C to -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Anti-C4d Antibody (FITC) Assay Protocol
[C4d]FlowPRA Test Using FITC-conjugated Anti-human C4d Antibody (C4dpAb2)
The FlowPRA® Screening test (One Lambda, Inc., Canoga Park, CA, USA) consists of a pool of 30 different microbead preparations coated with either purified HLA class I or HLA class II antigens from different cell lines covering all common HLA antigens. According to the manufacturer´s protocol this assay is applicable for detection of anti-HLA class I or II IgG alloreactivities (Ref. 1). The [C4d]FlowPRA test was developed for detection of anti-HLA alloantibody-triggered C4d deposition to FlowPRA® beads by FITC-conjugated anti-human C4d antibody. As an adjunct to standard FlowPRA® screening, this test allows for selective detection of presumably more harmful classical complement-activating anti-HLA alloantibodies. The [C4d]FlowPRA test may represent a specific alternative to conventional complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) PRA testing (Ref. 2).
Read the entire protocol before beginning the test.
|
1. |
Incubate negative control serum or test serum (9 μl) with 0.5 μl FlowPRA® class I and 0.5 μl FlowPRA® class II beads*. |
|
2. |
Incubate for 30 minutes on ice. |
|
3. |
Add 30 µl serum obtained from a nonsensitized healthy male volunteer with normal |
|
4. |
Incubate for 30 minutes on ice. |
|
5. |
Wash beads twice with cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). |
| 6. | Add 20 µL working dilution (1:25) of FITC-conjugated C4dpAb2 to 20 µl beads suspension (final dilution 1:50). |
|
7. |
Incubate for 30 minutes on ice. |
|
8. |
Wash beads twice with cold PBS and analyze by flow cytometry. |
|
9. |
The major bead population is gated on the forward-versus-side-scatter dot plot. Then, two gates are set on the FL2 histogram to separately analyze HLA class I-coated (FL2-negative) and class II (FL2 high-fluorescent)-coated populations. FITC conjugated anti-human C4d antibody binding to HLA class I or class II beads is evaluated on FL1 |
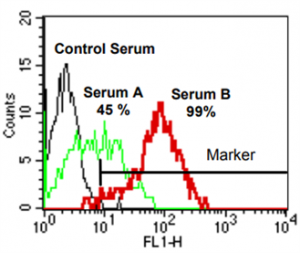
[C4d]FlowPRA (HLA class I) screening of representative sera (serum A, serum B) obtained from two presensitized patients. A FL-1 histogram (FlowPRA® HLA class I beads are gated) is depicted. The marker is set according to C4d staining obtained with a non-binding control serum. The percentage of positive events, which represents %[C4d]FlowPRA reactivity, is indicated for the two test sera.
Additional Reagents Required
*FlowPRA® Class I Screening Test, Cat. No. FL1-30
FlowPRA® Class II Screening Test, Cat. No. FL2-30
One Lambda, Inc., 21001 Kittridge, Canoga Park, CA 91303, USA, www.onelambda.com
Literature
 PMID: 15935890
PMID: 15935890 PMID: 9619770
PMID: 9619770C4d Function
Circulating alloantibodies encounter the grafted endothelium as the first target. Living endothelial cells can rapidly eliminate bound antibodies from the cell surface by “capping”, “shedding” or “internalisation”.
C4d is the degradation product of the activated complement factor C4, a component of the classical complement cascade, which is typically initiated by binding of antibodies to specific target molecules. Detection of C4d is regarded as an indirect sign, a “footprint” of an antibody response against the allograft. The majority of publications describe C4d as an important
biomarker in kidney transplantation but also in heart, liver, and other transplants.
-
Organ transplantation
- Kidney transplantation
- Liver transplantation
- Heart transplantation
- Lung transplantation
- Detection of T and B cells specific complement-fixing alloantibodies using flow cytometry: A diagnostic approach for a resource limited laboratory.
Jain, D., Dorwal, P., Pande, A., Tyagi, N., Mehra, S., Raina, V., 2017. Asian J Transfus Sci 11, 171–179.
PMID: 28970687; PMCID: PMC5613426
- Global quality assessment of liver allograft C4d staining during acute antibody-mediated rejection in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue.
Neil, D.A.H., Bellamy, C.O., Smith, M., Haga, H., Zen, Y., Sebagh, M., Ruppert, K., Lunz, J., Hübscher, S.G., Demetris, A.J., 2018. Human Pathology 73, 144–155.
PMID: 29288041
- Pros and cons for C4d as a biomarker.
Cohen, D., Colvin, R.B., Daha, M.R., Drachenberg, C.B., Haas, M., Nickeleit, V., Salmon, J.E., Sis, B., Zhao, M.-H., Bruijn, J.A., Bajema, I.M., 2012. Kidney International 81, 628–639.
PMID: 22297669
- Prospects and limitations of post-transplantation alloantibody detection in renal transplantation.
Böhmig, G.A., Bartel, G., Regele, H., Wahrmann, M., 2009. Human Immunology 70, 640–644.
PMID: 19375475
- Review article: Luminex technology for HLA antibody detection in organ transplantation.
Tait, B.D., Hudson, F., Cantwell, L., Brewin, G., Holdsworth, R., Bennett, G., Jose, M., 2009. Nephrology 14, 247–254.
PMID: 19207861
- In vitro detection of C4d-fixing HLA alloantibodies: associations with capillary C4d deposition in kidney allografts.
Bartel, G., Wahrmann, M., Exner, M., Regele, H., Huttary, N., Schillinger, M., Körmöczi, G.F., Hörl, W.H., Böhmig, G.A., 2008. Am. J. Transplant. 8, 41–49.
PMID: 17924995
- Antibodies, isotypes and complement in allograft rejection.
Böhmig, G.A., Bartel, G., Wahrmann, M., 2008. Current Opinion in Organ Transplantation 13, 411–418.
PMID: 18685338
- Antibody-Mediated Renal Allograft Rejection: Diagnosis and Pathogenesis.
Colvin, R.B., 2007. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 18, 1046–1056
PMID: 18685338
-
Pivotal Role of Complement-Fixing HLA Alloantibodies in Presensitized Kidney Allograft Recipients: Role of Complement-Fixing HLA Presensitization.Wahrmann, M., Exner, M., Schillinger, M., Haidbauer, B., Regele, H., Körmöczi, G.F., Hörl, W.H., Böhmig, G.A., 2006. American Journal of Transplantation 6, 1033–1041.
PMID: 16611341
- Complement C4d in Graft Capillaries - the Missing Link in the Recognition of Humoral Alloreactivity.
Feucht, H.E., 2003. American Journal of Transplantation 3, 646–652.
PMID: 12780555
- The Clinical Importance of Alloantibody-Mediated Rejection.
Halloran, P.F., 2003. American Journal of Transplantation 3, 639–640.
PMID: 12780552
- Kidney transplants, antibodies and rejection: is C4d a magic marker?
Nickeleit, V., 2003. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 18, 2232–2239.
PMID: 14551348
- Humoral Theory of Transplantation.
Terasaki, P.I., 2003. American Journal of Transplantation 3, 665–673.
PMID: 12780557
- Humoral rejection in kidney transplantation: new concepts in diagnosis and treatment.
Mauiyyedi, S., Colvin, R.B., 2002. Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension 11, 609–618.
PMID: 12394606
- Immunoadsorption Combined with Membrane Filtration to Counteract Early Treatment-Refractory Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Doberer, K., Bond, G., Kläger, J., Regele, H., Strassl, R., Reindl-Schwaighofer, R., Scheriau, G., Wahrmann, M., Kikić, Ž., Faé, I., Fischer, G., Böhmig, G.A., Eskandary, F., 2020. BPU 1–10.
- Detection of T and B cells specific complement-fixing alloantibodies using flow cytometry: A diagnostic approach for a resource limited laboratory. Jain, D., Dorwal, P., Pande, A., Tyagi, N., Mehra, S., Raina, V., 2017. Asian J Transfus Sci 11, 171–179.
PMID: 28970687; PMCID: PMC5613426
- C4d FlowPRA is a useful tool in live related renal transplants. Dorwal, P., Pande, A., Mehra, S., Tyagi, N., Jain, D., Raina, V., 2014. Pathology 46, 471–472.
PMID: 24977744
- In vitro detection of C4d-fixing HLA alloantibodies: associations with capillary C4d deposition in kidney allografts. Bartel, G., Wahrmann, M., Exner, M., Regele, H., Huttary, N., Schillinger, M., Körmöczi, G.F., Hörl, W.H., Böhmig, G.A., 2008. Am. J. Transplant. 8, 41–49.
PMID: 17924995
 Download biomedica product list
Download biomedica product list